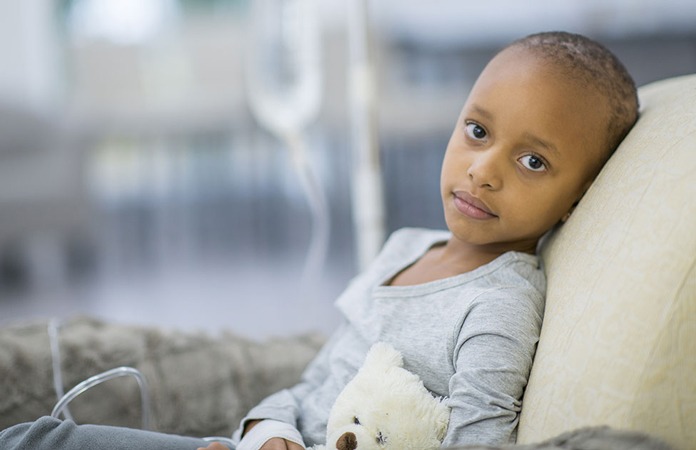
What Are Lymphoblasts and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia?
Lymphoblasts are a form of lymphocytes. They are immature white blood cells that play an important in the immune system. These cells are produced in the bone marrow through hematopoiesis. In this process, a hematopoietic stem cell may evolve along the lymphoid line or myeloid line. This results in the production of the lymphoblasts. When these cells progress, they may become B cells, T cells, or NK cells. [1]
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a type of leukemia or blood cancer. It particularly affects the early production of white blood cells called lymphocytes. When the condition progresses, more immature lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow than mature cells. Because white blood cells play a key role in the immune system, acute lymphoblastic leukemia may affect the body’s ability to fight against infections. It is estimated that this form of leukemia occurs in around 30 out of one million kids in the U.S. Among them, most cases are reported in those from 3 to 5 years old. Fortunately, many treatment options are available to improve the symptoms. [2]