Cystitis
Cystitis refers to inflammation of the bladder, which is a hollow organ storing urine from the kidney. In most cases, cystitis is caused by a bacterial infection. Other triggers could also increase the risk of having cystitis, such as bladder stone, pregnancy, enlarged prostate glands, menopause, diabetes, friction from sex, bladder surgery, chemical irritants, etc. Though the condition is more likely to be seen in women, everyone could develop cystitis.
Symptoms of cystitis often appear as:
- Burning sensation during urination
- Persistent urge to pee
- Frequent urination with a small amount of urine
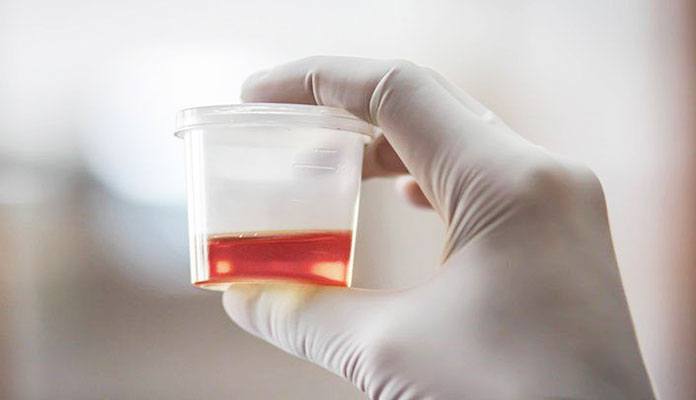
- Cloudy urine or dark urine with a bad odor
- Hematuria: blood in the urine
- Discomfort in the pelvis and lower abdomen
- Low-grade fever
People with mild symptoms could often recover on their own in a few days. If your symptoms are not clearing up, please seek medical advice immediately. The reason is that the bacterial infection could backtrack deeper from your bladder to your kidneys, causing kidney infection. Kidney infection is more severe and sometimes could lead to permanent kidney damage. [3]