What Is Plasma Cell Leukemia?
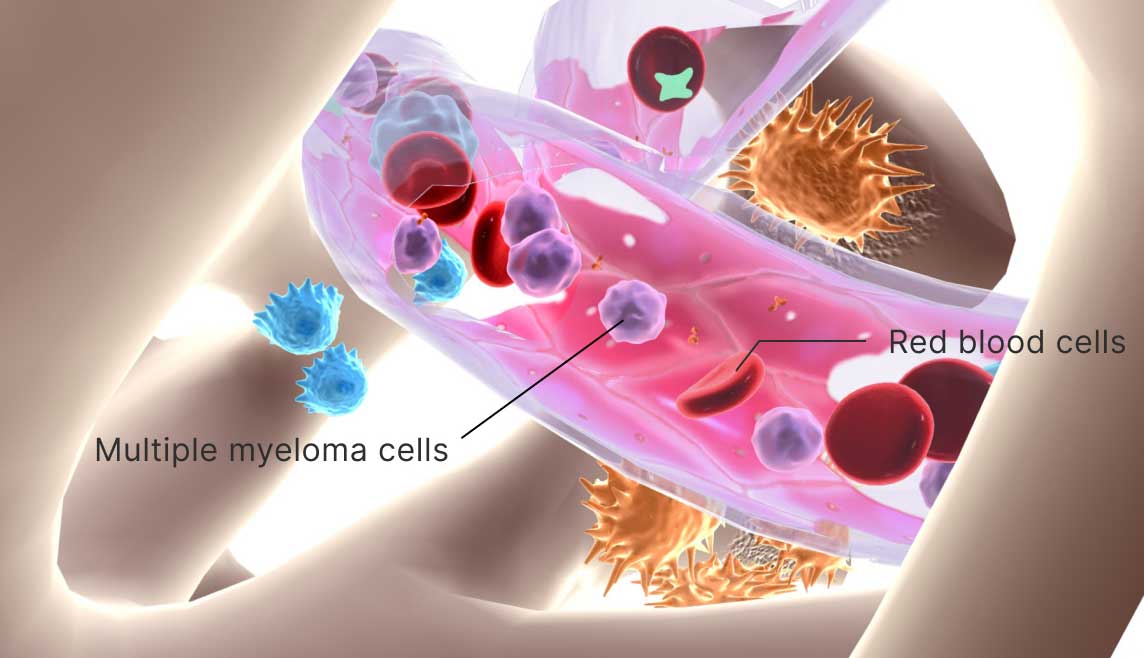
Plasma cell leukemia or plasma cell myeloma is an aggressive form of cancer that causes excessively high numbers of abnormal plasma cells in the bloodstream. The condition is quite rare and affects the cells in the bone marrow. In people with this disease, plasma cells grow uncontrollably and become abnormal. Plasma cell leukemia is a form of multiple myeloma. It may evolve from advanced myeloma or start by itself. [1]
Multiple Myeloma and Plasma Cell Leukemia
Plasma cell leukemia is a rare form of multiple myeloma, which occurs when plasma cells inside the bone marrow multiply uncontrollably. Bone marrow is spongy and responsible for producing blood, stem cells, and other substances. In people with multiple myeloma, the immune system, bones, and other organs may become weaker. Anemia could happen as well. While multiple myeloma is common, plasma cell leukemia is rare and affects only one in every million individuals without a history of cancer each year. Compared to multiple myeloma, plasma cell leukemia is also more aggressive with average survival rates being around one year after diagnosis. Many new treatment options may improve the long-term outlook for those with plasma cell leukemia. However, the overall outlook of Plasma cell leukemia remains quite poor compared to multiple myeloma. [2]